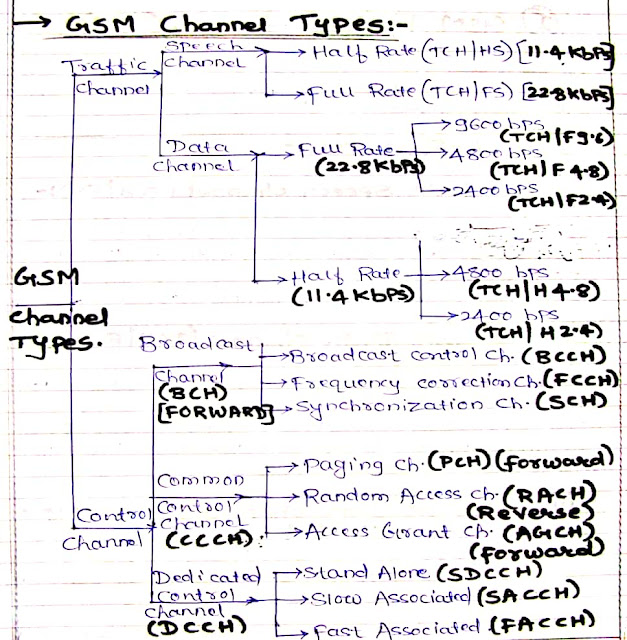
GSM control channel (CCH):
1) Broadcast channel (BCH):
(a) Broadcast control channel (BCCH):
(b) Frequency correction channel (FCCH):
The FCCH allows each subscriber unit to synchronize its internal frequency standard (local oscillator) to the precise frequency of the bottom station.
(c)Synchronization channel (SCH):
(d) Common control channel (CCCH):
(a) Paging channel (PCH):
The PCH provides paging signals from the BS to all or any mobiles within the cell, and notifies a selected mobile of an incoming call which originates from PSTN. PCH may be wont to provide cell broadcast ASCII text messages to all or any subscribers.
(b) Random Access Channel (RACH):
The RACH may be a reverse link channel employed by a subscriber unit to acknowledge a page from the PCH and is additionally employed by mobiles to originate a call.
(c) Access grant channel (AGCH):
The AGCH is employed by the BS to supply forward link communication to the mobile, and carries data which instructs the mobile to work during a particular physical channel.
(e) Dedicated control channel (DCCH):
(a) Stand-alone Dedicated control channel (SDCCH):
The SDCCH carries signaling data following the connection if the mobile with the BS, and just before TCH assignment issued by the BS. The SDCCH ensures that the mobile station and base station remain connected while the BS and MSC verifies subscriber unit.
(b) Slow Associated Control Channel (SACCH):
On the forward link the SACCH is employed to send slow but regularly changing control information to the mobile such a transmit power level instruction. On the reverse link the SACCH carries information about the received signal strength.
(c) Fast Associated Control Channel (FACCH):
FACCH carries urgent messages and contains essentially an equivalent sort of information as SDCCH.









0 comments:
If you have any doubts,please let me know