Bluetooth state model
- A Bluetooth device can be in different operating states or modes. It can move from one state to the other depending on the operational requirements.
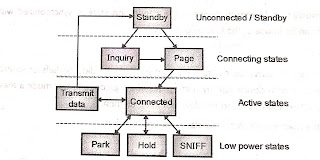 |
| Bluetooth State Model |
- Shows the above figure Bluetooth state model.
- The state or mode of any Bluetooth device can be classified into two types:
- Standby mode The device in standby state is not active, unconnected or in the standby mode.
- Connection mode
- A Bluetooth device in the connection state is synchronized with a piconet Standby mode. Such a device can be in one of the following modes:
a) Active mode
- A Bluetooth device in active mode transmits and receives the data packets or control packets. In this mode the Bluetooth device actively participates in the piconet. In this mode a master can tella slave, when it will be addressed and the slave will sleep till then.
- In this mode the master polls the active slaves for transmission.
b) Hold mode:
- The hold, park and sniff modes are power saving modes of Bluetooth operation. They are low power modes of the device.
- In order to maintain an intermediate power efficiency, it is necessary to use the hold mode. Power efficiency is improved by inactivating a device for short interval of time with the help of a timer.
- In this mode the slave does not support the ACL packets temporarily however it will support the SCO links.
- In this mode a device can perform the functions like scanning, paging, inquiring and attending other piconets
c) Park mode:
- If a slave wants to remain inactive for some time, it enters into the park mode. Such a slave device maintains synchronization with the master in a piconet, but it will not take part in the data traffic.
- This is a very low power mode. The slave gives up its active member address and a parked member address. However it stays synchronized.
- This mode not only saves the power but it also helps the master to have more than one slaves in a piconet.
- If a message is to be given to a parked device, it is sent over the broadcast channel characterized by an active member address of all zeros.
d) Sniff mode:
- As compared to park and hold mode, a device in Sniff mode has least power efficiency and highest duty cycle. With decreasing duty cycle, the power efficiency is increased. It can prolong battery life of device by reducing unnecessary transmission of poll packets.
- In this mode the listening activity of the slave is reduced. The master sends a command to the slave to enter into the sniff mode and gives it a sniff interval. The slave can listen to the transmissions only during these fixed intervals.
- Above the fig. shows the state model of BT which illustrates the relationship between different connections mode.








0 comments:
If you have any doubts,please let me know